Building Information Modeling
BIM
BIM stands for Building Information Modeling, and it is a digital process that involves creating and managing a virtual representation of a building or infrastructure project. BIM goes beyond traditional 3D modeling by incorporating rich data and information related to various aspects of the project, such as design, construction, operation, and maintenance. The goal of BIM is to improve collaboration, decision-making, and efficiency throughout the entire lifecycle of a construction project.
BIM models
What are they used for?
BIM models are used in various stages of a building or infrastructure project’s lifecycle, from design and construction to operation and maintenance. BIM technology has revolutionized the way projects are managed, coordinated, and executed, providing numerous benefits to all stakeholders involved. Here are the key stages and uses of BIM models:
Key stages and uses of BIM models:
- Conceptual Design: In the early stages of a project, BIM models are used for conceptual design. Architects and designers create 3D models to visualize design concepts and communicate ideas to clients and project stakeholders.
- Detailed Design and Documentation: BIM models serve as a basis for detailed design and documentation. Architects, engineers, and other professionals work collaboratively to create a comprehensive and coordinated set of construction documents using the BIM model.
- Coordination and Clash Detection: BIM models are utilized to coordinate the work of different disciplines involved in the project, such as architectural, structural, and mechanical design. Clash detection tools identify potential clashes and conflicts between various building elements, helping to resolve issues before construction begins.
- Quantity Takeoffs and Cost Estimation: BIM models contain detailed information about building elements, materials, and quantities. This data is used to perform quantity takeoffs and accurate cost estimations, helping with budgeting and cost control during the project.
- Energy Analysis and Sustainability: BIM can be used for energy analysis and sustainability assessments. The model is used to evaluate the building’s energy performance and explore design strategies to improve its energy efficiency and environmental impact.
- Virtual Reality and Simulation: BIM models can be utilized in virtual reality (VR) simulations to provide immersive experiences and visualize designs in a more interactive way. Simulation tools allow engineers to conduct analyses, such as structural, thermal, or lighting simulations, to optimize building performance.
- Construction Planning: BIM models aid in construction planning and scheduling. The 4D BIM approach combines the 3D model with the construction schedule, enabling better sequencing and coordination of construction activities.
- Construction Management: During construction, BIM models are used to track progress, manage construction sequencing, and identify potential issues that may arise during the construction process.
- Facilities Management and Operation: After construction, BIM models are handed over to facility managers to assist in ongoing operations and maintenance. The model contains valuable information about building components, equipment, and maintenance schedules.
- Asset Management and Renovation: BIM models are valuable for asset management and renovation projects. The model provides an accurate representation of the building’s components, making it easier to plan renovations, upgrades, and replacements.
Overall, BIM models are versatile tools that support the entire lifecycle of a building or infrastructure project. They enhance collaboration, improve decision-making, and optimize project efficiency from conception to ongoing operation and maintenance.
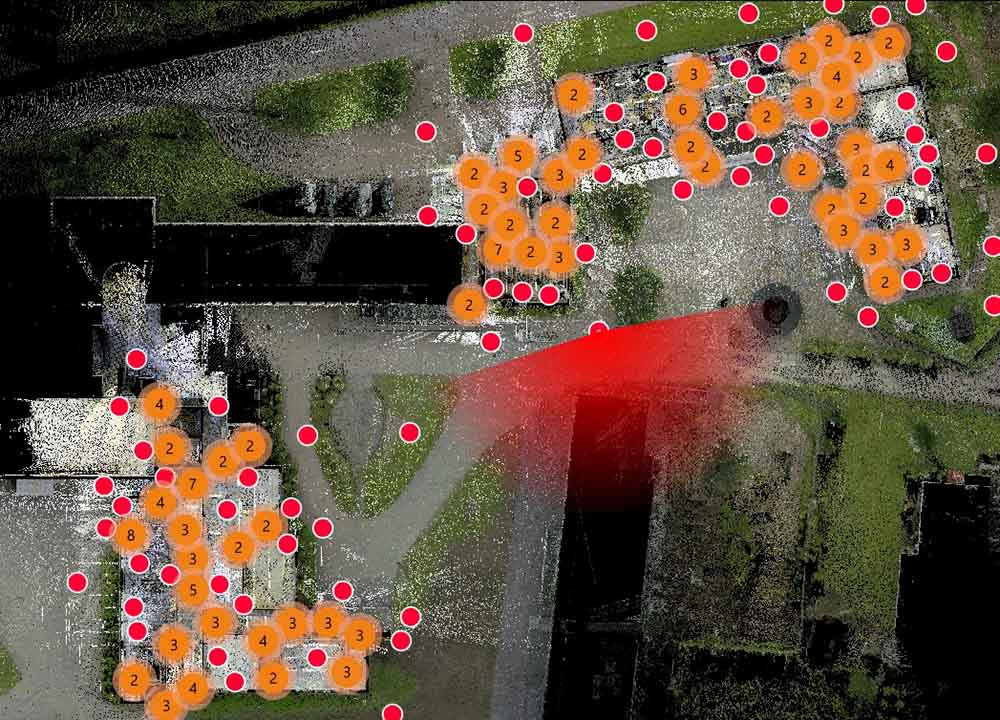
AS-BUILT BIM MODELS TRHROUGH REALITY CAPTURE
As-built BIM models, also known as post-construction BIM models or existing conditions BIM models, are digital representations of buildings or infrastructure projects that accurately capture the real-world conditions after construction is completed. These models are created by updating the original design BIM model with data and information obtained from on-site inspections, surveys, and reality capture technologies.
Here are some key characteristics and uses of as-built BIM models:
- Accurate Representation: As-built BIM models aim to be highly accurate and reflect the physical conditions of the constructed building or infrastructure as closely as possible. They incorporate changes, modifications, and variations that occurred during the construction process.
- Site Surveys and Reality Capture: To create as-built BIM models, site surveys and reality capture technologies like laser scanning, photogrammetry, or LiDAR are often used. These methods capture the physical environment in 3D, providing precise data for model creation.
- Comparison with Design Model: As-built BIM models are compared with the original design BIM model to identify any discrepancies between the planned design and the actual construction. This process helps detect any deviations or changes made during construction.
- Renovation and Retrofitting: As-built BIM models serve as a foundation for renovation or retrofitting projects. Architects and engineers can use these models to plan and visualize modifications or upgrades to the existing structure.
- Facilities Management and Operations: After construction, as-built BIM models are handed over to facility managers and owners. These models become valuable tools for facilities management, maintenance planning, and asset management.
- Asset Information and Data: As-built BIM models contain detailed information about building components, equipment, and systems. This information assists in tracking equipment specifications, warranty periods, maintenance schedules, and other essential data.
- Clash Detection and Coordination: As-built BIM models can be used for clash detection and coordination of new elements that need to be integrated into the existing structure. This ensures that new installations do not conflict with existing components.
- Historical Documentation: As-built BIM models serve as historical documentation of the building or infrastructure project. They provide a record of the construction process and any changes made during the project’s lifecycle.
- 3D Visualization and Simulation: As-built BIM models support 3D visualization and simulation, allowing stakeholders to understand the physical environment better. Virtual walkthroughs and simulations aid in decision-making and planning.
- Future Renovation and Maintenance: As-built BIM models become valuable resources for future renovations and maintenance activities. They provide a comprehensive understanding of the existing conditions, guiding future projects efficiently.
In summary, as-built BIM models are essential tools for capturing and documenting the physical state of buildings and infrastructure projects after construction. They play a critical role in facility management, renovation planning, and ensuring that the as-built conditions align with the original design intent.
Interested?
Get in touch

Sami Kinttu
Interested?
Leave us a message
If you'd like to get in touch, leave us a message and we'll get back to you as soon as possible.